Green Preservation Technologies
Reducing Spoilage and Energy Use
These methods extend the shelf life of products and enhance safety with less reliance on high heat, chemical preservatives, or high energy consumption, which directly reduces product waste.
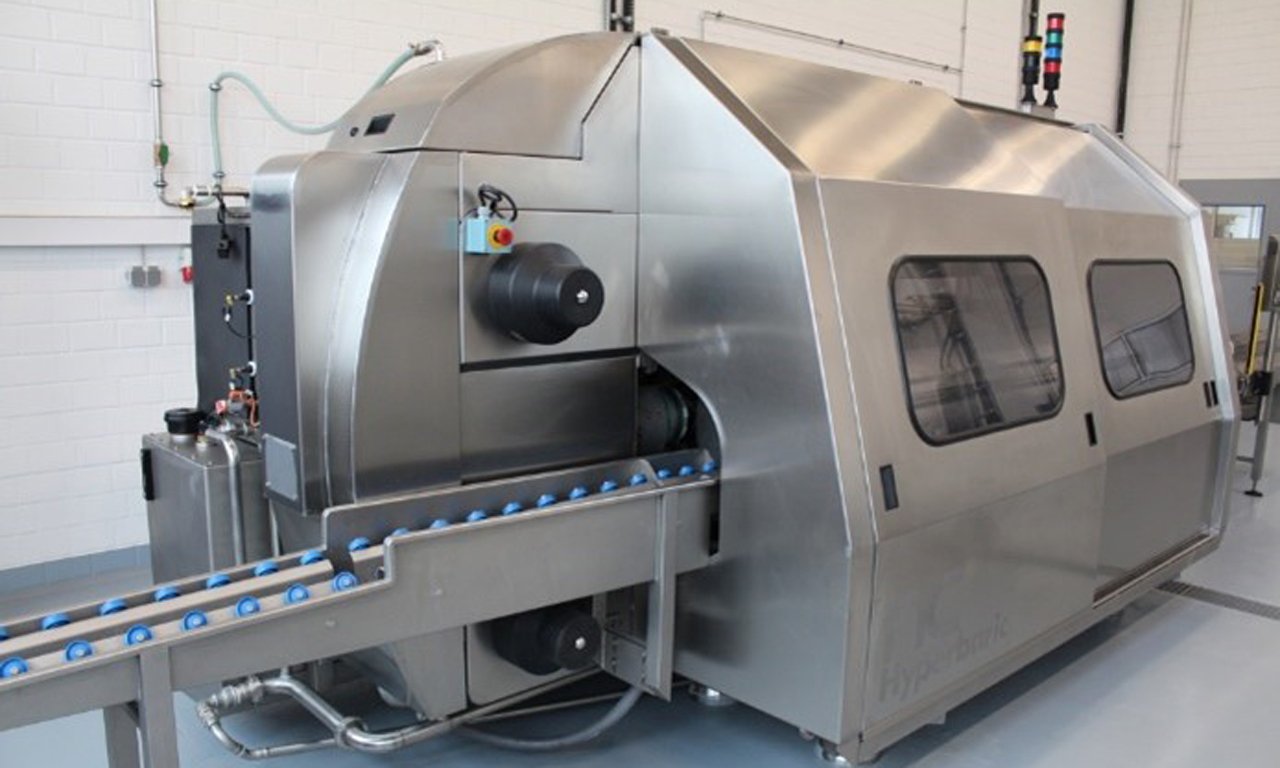

High-Pressure Processing (HPP):
- Mechanism: Products are subjected to extremely high hydrostatic pressure (using water) to inactivate pathogens and spoilage microorganisms.
- Sustainability Benefit: It’s a non-thermal technique, meaning it requires less energy than traditional heat pasteurization and better preserves the meat’s nutritional value, color, and flavor, reducing the chance of aesthetic-related waste
Pulsed Electric Field (PEF) Processing:
- Mechanism: Meat is treated with short, high-voltage electrical pulses.
- Sustainability Benefit: A low-energy, non-thermal alternative for microbial control. It can also improve the extraction of valuable compounds from by-products and enhance processing efficiency (e.g., accelerating curing or marination).
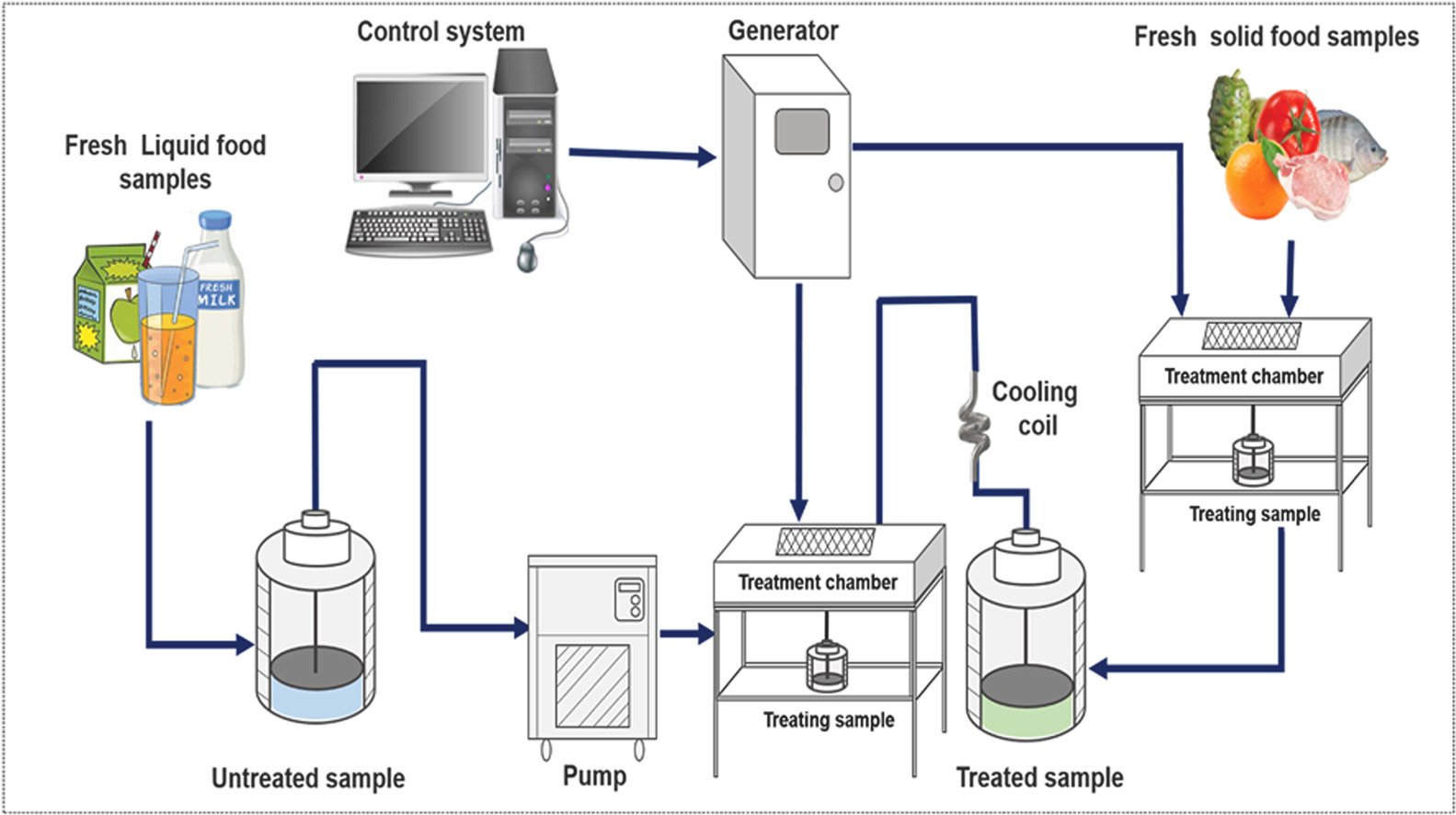
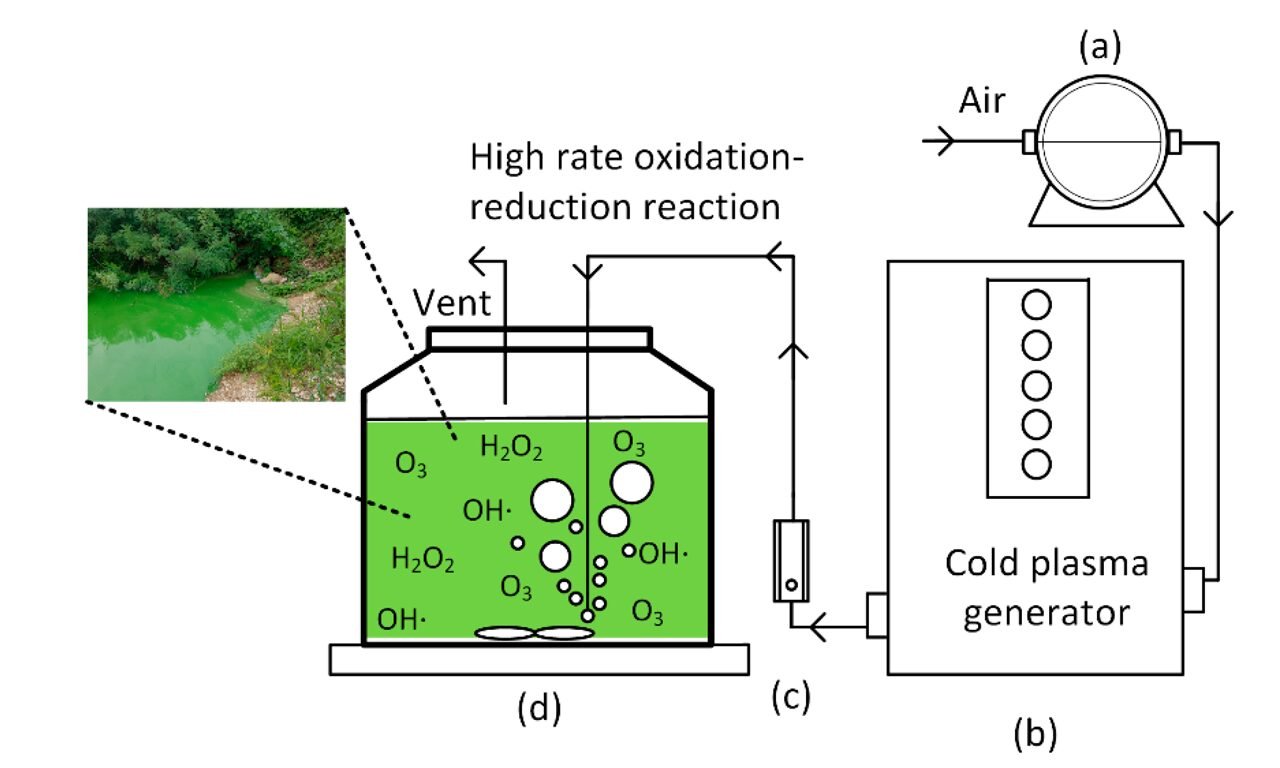
Cold Plasma and UV Treatment:
- Mechanism: Cold plasma uses ionized gas for surface decontamination, while UV light is used to disinfect meat surfaces and processing water/materials.
- Sustainability Benefit: Both are chemical-free methods for reducing microbial load, which improves food safety and extends shelf life without the need for chemical agents or excessive water.
Waste-to-Resource Strategies
Utilizing By-products
These techniques focus on transforming materials traditionally considered waste (blood, bones, fat, wastewater) into valuable co-products, achieving a circular economy model.
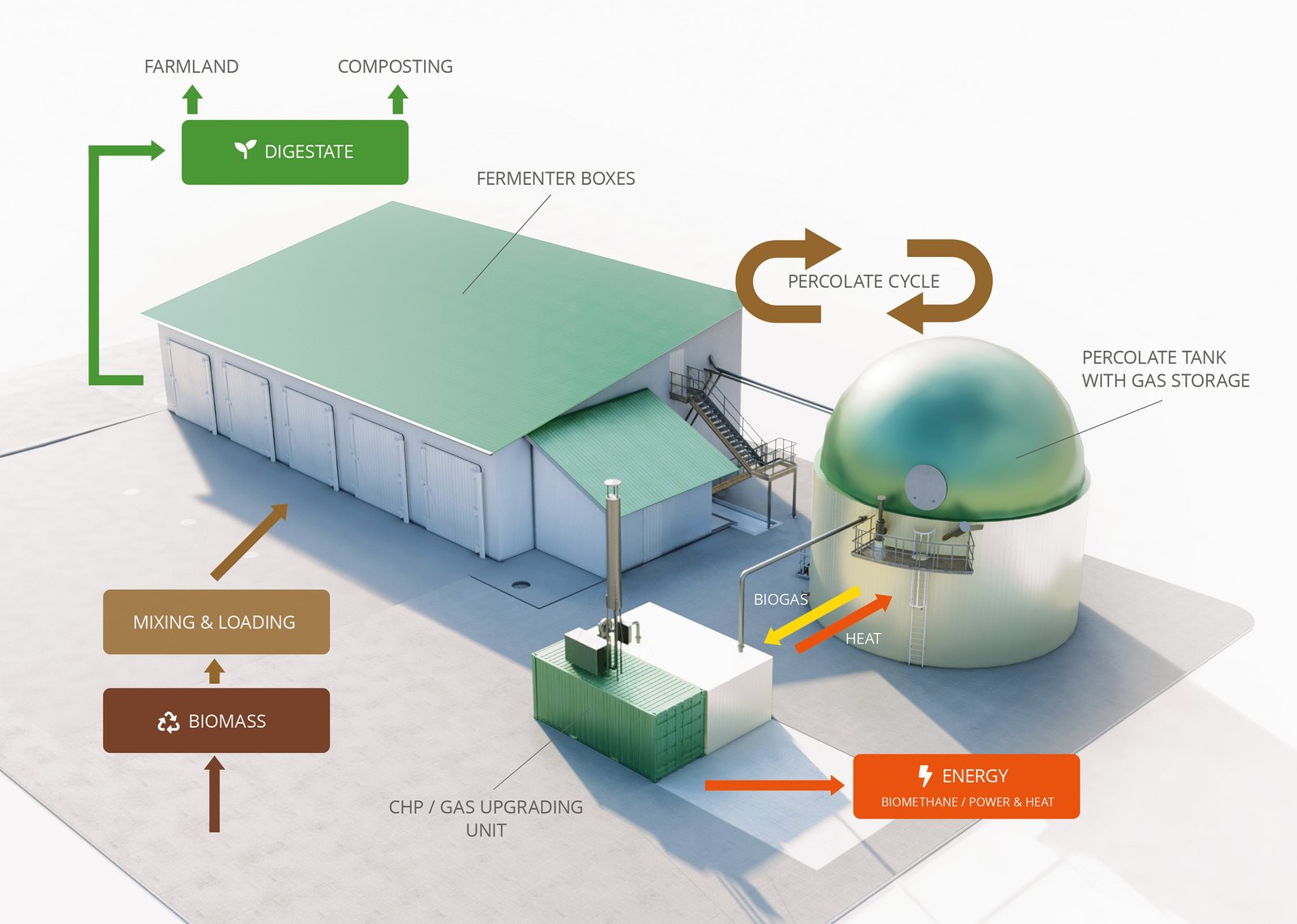
Anaerobic Digestion (AD) for Biogas Production:
- Mechanism: Organic waste (including blood, fats, and wastewater sludge) is broken down by microorganisms in an oxygen-free environment.
- Sustainability Benefit: The process generates biogas (a renewable energy source) that can be used to power the processing plant, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. The remaining material (digestate) can often be processed into a nutrient-rich fertilizer.
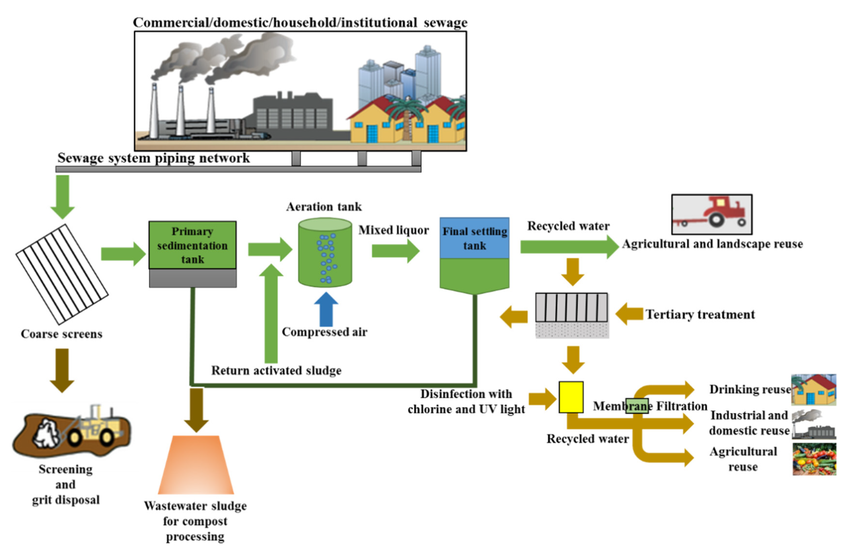
Advanced Water Reclamation:
- Mechanism: Wastewater is treated using systems like Membrane Filtration (ultra- or nanofiltration) and UV disinfection.
- Sustainability Benefit: These technologies produce high-quality, reclaimed water that can be safely reused in non-contact areas of the processing plant (e.g., cleaning), drastically cutting down on freshwater consumption.
Maximizing By-product Valorization (Rendering and Upcycling):
- Mechanism: Instead of simply disposing of non-meat components, advanced rendering converts things like fat, bones, and trimmings into high-value products.
- Sustainability Benefit: Fats are turned into tallow or biodiesel; bones and trimmings are converted into protein meals for animal feed, pet food, or even specialty products like gelatin or collagen, maximizing the yield from every animal and diverting nearly all organic material from landfills.